5.3.2 Plymouth Sound to Fowey: Main Activities and Uses

Plymouth Sound is heavily used by naval and other military operations, commercial shipping and the fishing industry.
The case study area adjoins one of the world’s busiest shipping routes, the English Channel. Plymouth hosts the UK’s largest naval base, as well as having a commercial and a fishing port. Other parts of the case study site are used for coastal cargo and cruise shipping, although this is limited by the small size and available infrastructure of the other harbours in the area, Fowey and Looe. Commercial fishing vessels also operate out of Fowey and Looe, as well as Polperro. Military exercises take place on the coast at Whitsand Bay and Tregantle Fort and offshore along the case study.

Like much of the rest Cornwall and Devon, tourism and recreation are an important activity throughout the year, but concentrated in the summer season and shoulder months.
The following figure illustrates some of the coastal and marine recreational activities that occur in the case study area. Running through the entire stretch of the study site is the South West Coast Path, providing access to this part of the Cornish coast and its many beaches.
Walkers and visitor numbers vary along the path’s route, with the easterly sections of the coast path to Rame Head less well visited.
The towns of Looe, Polperro and Fowey are significant tourist attractions. Indeed, Fowey Harbour receives a growing number of cruise ship visits each year.
The area is considered important from a maritime cultural heritage perspective, due the large number of wrecks within the site. Scuba diving associated with these wrecks, including the HMS Scylla artificial reef. Yachting and recreational boating are also very popular with associated moorings, marinas and slipways.
Both shore-based and boat-based angling occurs, with a number of angling competitions held throughout the year. There are a number of culturally significant landmarks in the area including the Eddystone lighthouse, Plymouth Breakwater, Rame Head Chapel, Tregantle Fort and St Catherines Castle. The area has long been an inspiration for art and literature.
A range of commercial fishing occurs, including demersal and benthic, along with potting and traps for shellfish.
Within the case study there are two designated areas for disposing of estuarine dredged sediments. One spoil site is situated south west of Rame Head, the other South East of Gribben Head.
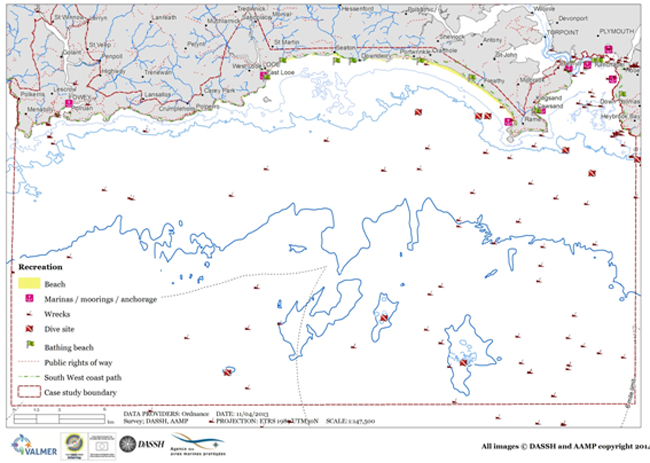 Figure: Map showing a number of recreational sites within the case study (MBA-DASSH, 2014)
Figure: Map showing a number of recreational sites within the case study (MBA-DASSH, 2014)

