5.3.7 Plymouth Sound to Fowey: Methods and Results

The Ecosystem Services Assessment was undertaken by Plymouth Marine Laboratory in collaboration with the Marine Biological Association of the UK who provided data and GIS mapping support.
Whilst this approach used existing data, the project added considerable value through its Data Discovery exercise, processing, analysis and presentation/visualisation for a baseline assessment. An additional discrete piece of research to quantify, map and visualise the health and wellbeing benefits associated with Plymouth Sound to Fowey area was undertaken by the University of Exeter [Willis et al., 2014].

A primarily qualitative assessment was made of how services might change under the management scenarios.
The baseline assessment of multiple services was refined to focus on nursery habitats for commercial species, carbon storage, sea defence and waste processing (considering the supply of clean water, immobilisation of pollutants and nutrient cycling). This component of the study took a spatial approach, mapping the delivery of the services based on information within the literature concerning linkages between habitats and services.
Some quantification and monetary valuation was however undertaken for carbon storage.
The assessment of cultural services [Willis et al., 2014] used an online and face-to-face survey with local residents, containing a spatial component in which each respondent was asked to indicate three locations that were considered special, significant or valuable and three that were unpleasant, neglected or challenged.
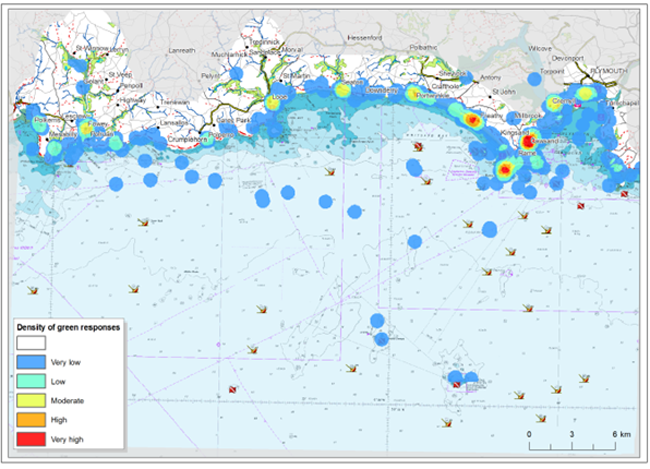
Figure: Significant and valuable places in the Sound to Fowey case study identified by survey respondents
- The baseline maps of ecosystem service delivery illustrated the importance of Plymouth Sound, with its varied habitats, as a nursery for a range of commercial species.
- The sand and coarse habitats that cover much of the case study site provided negligible levels of carbon storage relative to other habitats, although value of the site for carbon storage nonetheless amounts to £1.4million per year. These habitats play a greater role in nutrient cycling and the provision of clean water.
- The value of the increased carbon storage through the recovery of seagrass following the replacement of swing moorings is unlikely to offset the costs of installing the new eco- buoys, although the values of other services that may also increase were not calculated.
- The dredge disposal scenario identified the potentially large increase in cultural services that could be obtained from relocation of the disposal site, while the Marine Protected Area scenario highlighted the complex trade-offs that would require consideration in any management decision.

