3.9.2 Bayesian belief networks


Example
A Bayesian Belief Network model was used to examine the effects of current fishing pressure and hypothetical management scenarios on the subtidal sediments in the North Devon Biosphere Reserve [Langmead et al., 2015].
A Bayesian Belief Network model in the North Devon Biosphere Reserve case study
Three ecosystem services were considered: nursery habitats for commercial fish and shellfish, waste processing and carbon storage. The habitats across the North Devon Biosphere Reserve were divided into six broad habitat types and mapped.
The potential contribution of each habitat type to the supply of each service was determined using a four-point qualitative scale (negligible, low, moderate, significant), with the results based on a literature review (nursery habitats), empirical evaluation of community bioturbation potential (waste processing), and considering the sediment mud content (carbon storage).
The sensitivity of the services to key pressures was also determined (see Sensitivity assessment section ![]() ). Information on existing levels of fishing activity was combined with the sensitivity information to model the current supply of each ecosystem service in each 1km2 grid cell across the area.
). Information on existing levels of fishing activity was combined with the sensitivity information to model the current supply of each ecosystem service in each 1km2 grid cell across the area.
The model was then run again based on the change in pressures that would be exerted by three management scenarios: the establishment of marine protected areas, aggregate extraction and the development of extensive mussel aquaculture. The scenarios included the implications of these scenarios for the displacement of fishing effort.
The model outputs suggested that ecosystem service supply increased within the proposed Marine Protected Area sites, although a decrease in service delivery was observed in the adjacent areas to which fishing effort was displaced.
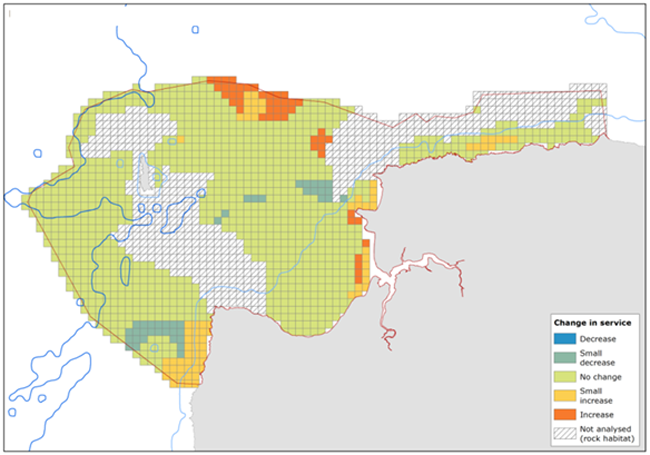 Figure: Model output showing the change in combined ecosystem services following the establishment of marine protected areas
Figure: Model output showing the change in combined ecosystem services following the establishment of marine protected areas
Both the aggregate extraction and aquaculture scenarios resulted in a decrease in nursery habitat, but the latter also showed potential large increases in carbon storage and waste processing.


